Understanding Osteoarthritis and the Role of Supplements
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage deterioration, inflammation, and pain. As the most common form of arthritis, it affects millions worldwide, particularly older adults and those with joint injuries or genetic predispositions. While no definitive cure exists, various treatments aim to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and slow cartilage degradation. Among these, dietary supplements play a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis symptoms and potentially supporting cartilage repair. Scientific advancements have led to the identification of specific compounds that can enhance joint health, reduce inflammation, and promote mobility. Understanding the best supplements for osteoarthritis is essential for individuals seeking alternative or complementary therapies to traditional treatments.
You may also like: How Do I Know What Vitamins I Need? A Guide to Safe, Effective Dietary Supplements Backed by Science
Glucosamine and Chondroitin: Essential Cartilage Support
Glucosamine and chondroitin are two of the most extensively studied supplements for osteoarthritis. Glucosamine is a naturally occurring compound found in joint cartilage and plays a vital role in maintaining its structure and integrity. Chondroitin, often paired with glucosamine, is a fundamental component of cartilage that helps retain water, enhancing its shock-absorbing capabilities. Numerous studies suggest that these supplements may help slow cartilage breakdown, reduce joint pain, and improve function in individuals with osteoarthritis. While the effectiveness varies among individuals, long-term use has been associated with better joint health outcomes. The combination of these compounds is widely available in tablet, capsule, and powder forms, making them convenient for daily supplementation.
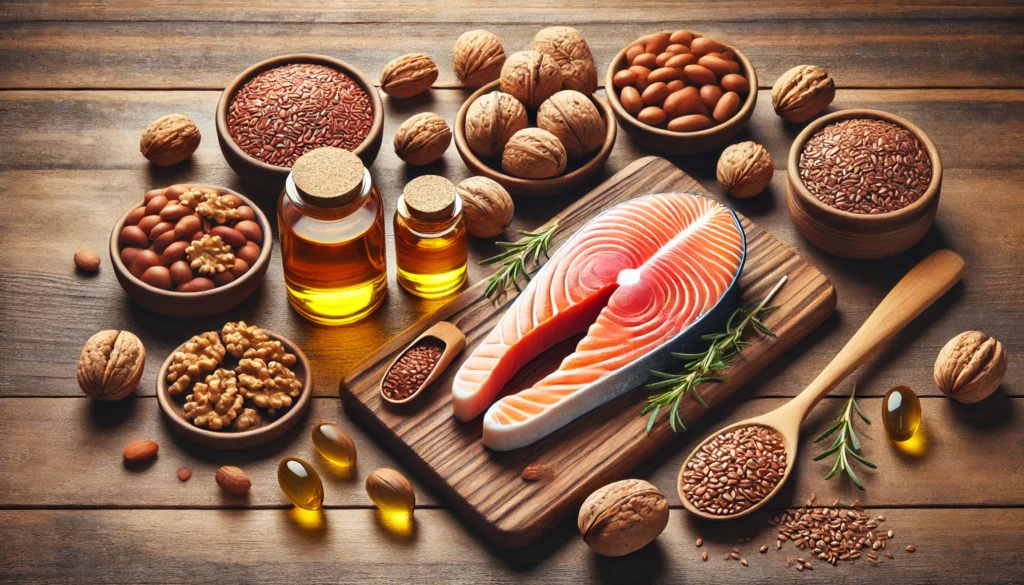
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Potent Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly derived from fish oil, are well known for their powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation contributes significantly to osteoarthritis progression, leading to pain and stiffness in affected joints. The two primary omega-3 fatty acids—eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)—have been shown to reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines and enzymes that degrade cartilage. Clinical research indicates that individuals supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids experience reduced joint stiffness and pain, as well as improved overall joint function. In addition to fish oil, sources such as flaxseed, walnuts, and algae-derived supplements provide plant-based omega-3 options for those who prefer vegetarian alternatives.
Curcumin: A Natural Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has gained significant attention for its ability to modulate inflammation and pain. As a natural polyphenol, curcumin inhibits key inflammatory pathways associated with osteoarthritis, offering relief similar to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) but with fewer side effects. Studies suggest that curcumin supplementation can decrease joint stiffness and swelling, providing a natural alternative for managing osteoarthritis symptoms. However, curcumin has low bioavailability, meaning that the body does not absorb it efficiently. To enhance its effectiveness, many formulations include piperine, a black pepper extract that increases curcumin absorption. Regular supplementation can contribute to improved joint comfort and mobility over time.

Collagen Peptides: Enhancing Cartilage Regeneration
Collagen is a primary structural protein in cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, making it a vital component for joint health. Hydrolyzed collagen peptides, derived from animal sources, provide the building blocks necessary for cartilage regeneration and repair. Research suggests that collagen supplementation can improve joint flexibility, reduce pain, and support overall connective tissue integrity. Collagen supplements often contain additional nutrients like vitamin C, which plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis. By incorporating collagen peptides into a daily routine, individuals with osteoarthritis can potentially enhance cartilage resilience and slow the degenerative process.
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM): A Natural Sulfur Compound for Joint Support
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is an organic sulfur compound known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Sulfur is a critical component of joint cartilage, contributing to its strength and elasticity. MSM has been shown to reduce joint pain and stiffness while promoting collagen formation and overall joint health. Clinical studies highlight its effectiveness in improving osteoarthritis symptoms, particularly when combined with glucosamine and chondroitin. MSM supplements are available in capsules, powders, and topical formulations, providing flexibility in how individuals choose to incorporate them into their wellness routine.
Vitamin D and Calcium: Essential Nutrients for Bone and Joint Health
Vitamin D and calcium are essential for maintaining strong bones and supporting joint function. Deficiencies in vitamin D have been linked to increased osteoarthritis risk and severity, as the vitamin plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and bone metabolism. Adequate calcium intake is necessary for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis, a condition that can exacerbate osteoarthritis symptoms. Supplementing with vitamin D and calcium ensures that bones remain strong and capable of supporting joint structures. Many individuals, especially those with limited sun exposure, benefit from vitamin D supplementation to optimize joint and bone health.
Hyaluronic Acid: Lubrication and Cushioning for Joints
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in synovial fluid, which provides lubrication and cushioning within joints. Osteoarthritis leads to a reduction in synovial fluid quality, contributing to increased friction and joint discomfort. Hyaluronic acid supplements have been found to improve joint lubrication, enhance shock absorption, and reduce pain in osteoarthritis patients. Some formulations are available in oral capsules, while others are administered through intra-articular injections by healthcare professionals. Regular supplementation with hyaluronic acid supports joint function and may help slow the progression of osteoarthritis.
Boswellia Serrata: Herbal Support for Joint Inflammation
Boswellia serrata, also known as Indian frankincense, is a potent herbal extract with strong anti-inflammatory properties. The active compounds in Boswellia, known as boswellic acids, inhibit pro-inflammatory enzymes that contribute to cartilage degradation and joint pain. Studies suggest that Boswellia supplementation can lead to significant improvements in pain reduction and mobility in osteoarthritis patients. Unlike conventional anti-inflammatory medications, Boswellia has fewer gastrointestinal side effects, making it a favorable natural alternative for managing joint discomfort.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Supplements for Osteoarthritis
1. Can supplements for osteoarthritis completely cure the condition?
While supplements for osteoarthritis can provide relief from symptoms and help slow disease progression, they do not offer a cure. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition that involves cartilage breakdown, and while certain osteoarthritis dietary supplements may support cartilage health and reduce inflammation, they cannot fully reverse the damage. The best supplements for osteoarthritis knee pain often include glucosamine and chondroitin, which help maintain joint function. However, long-term management should involve a combination of lifestyle changes, exercise, and dietary improvements alongside supplements to rebuild cartilage. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures that you select the most effective cartilage repair supplements tailored to your needs.
2. What are the key ingredients to look for in an osteoarthritis dietary supplement?
When selecting an osteoarthritis dietary supplement, key ingredients to consider include glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), and collagen. These compounds play essential roles in maintaining cartilage structure and joint lubrication. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil help reduce inflammation, making them one of the best supplements for osteoarthritis knee pain. Turmeric and curcumin are also widely recognized for their anti-inflammatory properties, potentially easing joint stiffness and discomfort. Always choose high-quality, clinically studied ingredients when selecting supplements for OA to ensure effectiveness.
3. How long does it take for supplements to rebuild cartilage and relieve symptoms?
The effectiveness of supplements for OA varies depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. Most people begin to notice improvements within 4 to 12 weeks of consistent use. Supplements to rebuild cartilage, such as glucosamine and chondroitin, take time to show noticeable benefits because they work by gradually enhancing joint health and reducing inflammation. Patience is key, and combining these supplements with a balanced diet and physical therapy can enhance their effectiveness. If no improvement is seen after several months, consulting a healthcare professional for alternative strategies is advisable.
4. Are there any side effects associated with vitamins for osteoarthritis?
Most vitamins for osteoarthritis, including vitamin D, C, and E, are generally safe when taken at recommended doses. However, some people may experience mild side effects such as stomach upset, nausea, or allergic reactions. Certain cartilage repair supplements, like glucosamine derived from shellfish, may cause allergic reactions in individuals with shellfish allergies. Additionally, excessive intake of fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D can lead to toxicity. Always adhere to dosage guidelines and consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
5. What is the role of collagen in managing osteoarthritis?
Collagen is a crucial component of cartilage and helps maintain joint integrity. Supplements for OA containing collagen peptides can support cartilage regeneration and reduce joint pain. Studies suggest that collagen supplementation improves mobility and reduces stiffness in individuals with osteoarthritis. When paired with other osteoarthritis dietary supplements like glucosamine and MSM, collagen can significantly enhance joint health. Collagen supplements are particularly beneficial for individuals looking to maintain long-term joint function and reduce cartilage breakdown.
6. Can food supplements for osteoarthritis replace a healthy diet?
No, food supplements for osteoarthritis should complement, not replace, a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients. A diet high in anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and berries plays a vital role in managing osteoarthritis symptoms. While the best supplements for osteoarthritis provide targeted support, they work best when combined with a nutrient-dense diet. A holistic approach that includes proper nutrition, exercise, and supplements to rebuild cartilage is essential for effective symptom management. Prioritizing whole foods alongside supplements ensures comprehensive joint support.
7. Are there specific supplements for osteoarthritis knee pain?
Yes, certain supplements are particularly beneficial for knee osteoarthritis. The best supplements for osteoarthritis knee pain include glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, MSM, and curcumin. These ingredients help reduce pain and inflammation while promoting cartilage repair. Omega-3 fatty acids also offer significant relief by reducing joint stiffness and enhancing mobility. Additionally, hyaluronic acid supplements can improve joint lubrication, making them a valuable addition to a knee osteoarthritis treatment plan. Using a combination of these supplements for OA can optimize knee joint health over time.
8. How do omega-3 fatty acids help with osteoarthritis?
Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, play a significant role in reducing inflammation associated with osteoarthritis. As one of the best supplements for osteoarthritis, omega-3s help decrease joint pain and stiffness by suppressing inflammatory markers. Regular intake of omega-3s may also slow cartilage degradation, making them effective supplements to rebuild cartilage. Many individuals with osteoarthritis benefit from combining omega-3s with other vitamins for osteoarthritis, such as vitamin D, to maximize joint protection. Including omega-3-rich foods like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts in the diet further enhances their effects.
9. Can supplements for OA interact with medications?
Yes, some supplements for OA can interact with medications, potentially altering their effectiveness. For instance, glucosamine and chondroitin may affect blood sugar levels, posing a concern for individuals with diabetes. Turmeric and fish oil, while beneficial as cartilage repair supplements, can have blood-thinning properties, which may interfere with anticoagulant medications. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new osteoarthritis dietary supplement, especially if you are taking prescribed medications. Being aware of potential interactions ensures safe and effective supplementation.
10. Are there natural alternatives to traditional supplements for osteoarthritis?
Yes, several natural alternatives can support joint health alongside traditional osteoarthritis dietary supplements. Herbal remedies such as Boswellia serrata, turmeric, and ginger have strong anti-inflammatory properties that help manage osteoarthritis symptoms. Additionally, certain foods like bone broth, rich in collagen, can act as food supplements for osteoarthritis by supporting cartilage health. Lifestyle changes, including weight management and low-impact exercise, also play a crucial role in preserving joint function. While these natural approaches can be effective, they are best used in conjunction with scientifically backed supplements to rebuild cartilage and slow disease progression.
Conclusion: Optimizing Joint Health with the Best Supplements for Osteoarthritis
Managing osteoarthritis effectively requires a multifaceted approach, and dietary supplements play a pivotal role in supporting joint health and cartilage repair. From glucosamine and chondroitin to omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, collagen peptides, and MSM, numerous scientifically backed options can help reduce inflammation, enhance mobility, and promote cartilage regeneration. Essential nutrients such as vitamin D, calcium, and hyaluronic acid further contribute to maintaining strong bones and lubricated joints. Additionally, herbal extracts like Boswellia serrata provide natural anti-inflammatory support. Choosing the right combination of supplements tailored to individual needs can significantly improve quality of life for those living with osteoarthritis. By integrating these dietary strategies with a healthy lifestyle, individuals can take proactive steps toward preserving joint function and minimizing discomfort, ultimately leading to improved mobility and well-being.
joint health supplements, arthritis pain relief, natural joint support, anti-inflammatory supplements, knee pain remedies, best vitamins for joints, cartilage regeneration, osteoarthritis pain management, mobility support supplements, turmeric for joint pain, glucosamine benefits, chondroitin for arthritis, MSM for joint health, collagen for joints, omega-3 for arthritis, natural remedies for osteoarthritis, supplements for joint stiffness, bone and joint health, holistic arthritis treatment, knee osteoarthritis relief
Further Reading:
12 Supplements for Osteoarthritis
Nutritional Supplements and Osteoarthritis
Do supplements help with the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While News7Health strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. News7Health, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of News7Health.