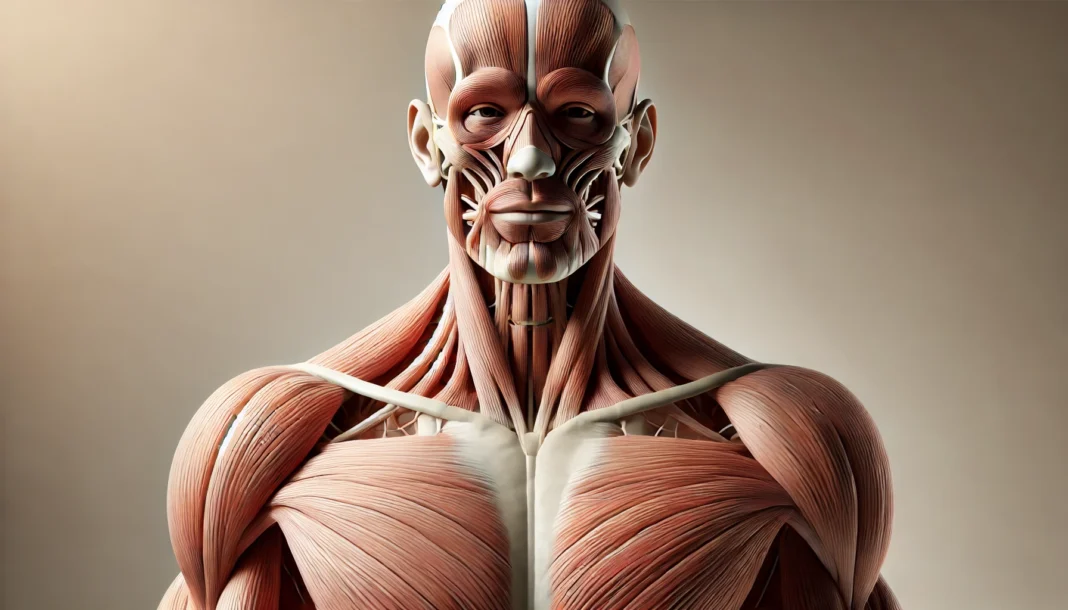
Introduction
The male body is a marvel of anatomical complexity, with a musculature designed for strength, agility, and endurance. Understanding the intricacies of male musculature is essential not only for those interested in fitness and bodybuilding but also for individuals seeking to improve their overall health and well-being. The human body muscle diagram serves as a vital tool for comprehending how muscles function in relation to movement, stability, and performance. Whether you are an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or simply curious about male anatomy muscles and bones, this guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of muscle groups, their roles, and their significance in physical health.
You may also like: Best Way to Build Muscle After 60: Proven Strategies for Strength and Longevity
Muscle anatomy is more than just an academic topic; it is crucial in injury prevention, rehabilitation, and optimizing physical performance. By analyzing the human body muscle diagram, one can gain deeper insight into how different muscle groups interact. Understanding these structures allows individuals to tailor their training routines, enhance recovery strategies, and ensure long-term musculoskeletal health. This guide delves into the fundamental aspects of male musculature, offering a detailed exploration of muscle types, functions, and their implications for overall well-being.
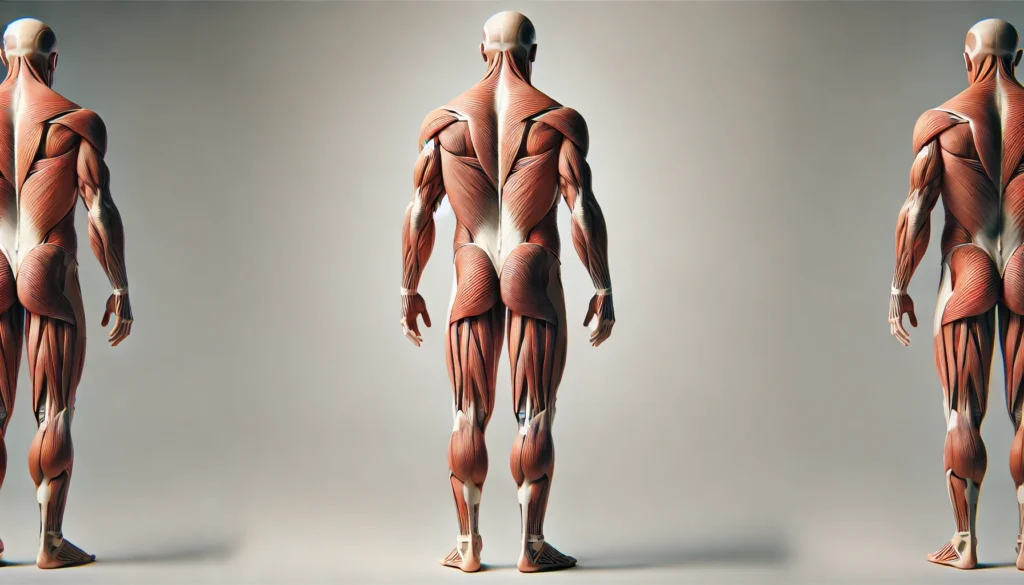
The Basics of Muscular Anatomy
Muscles are specialized tissues responsible for movement, posture, and force generation. They can be broadly categorized into three main types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Each plays a distinct role in bodily function, but skeletal muscles are the primary focus when discussing the human body muscle diagram, as they contribute most significantly to voluntary movements and strength.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and function through contraction and relaxation. These muscles work in pairs, where one muscle contracts while its opposing counterpart relaxes, allowing for smooth and controlled movement. This antagonistic muscle function is evident in actions such as flexing and extending the arm, where the biceps contract while the triceps relax. Understanding male musculature at this level is crucial for anyone seeking to improve physical fitness or recover from injuries.
Major Muscle Groups in the Male Body
The male anatomy muscles and bones form an interconnected system that facilitates movement and stability. The major muscle groups can be classified into different regions, each with unique functions and contributions to overall strength and coordination.
Upper Body Muscles
The upper body is composed of several significant muscle groups, including the chest, shoulders, back, and arms. These muscles play a vital role in strength training, functional fitness, and daily movement.
1. Pectoral Muscles: Commonly referred to as the chest muscles, the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor contribute to arm movement, pushing motions, and upper-body stability. Strengthening these muscles enhances upper-body power and improves posture.
2. Deltoids: The shoulder muscles, known as the deltoids, consist of three distinct heads: anterior, lateral, and posterior. These muscles facilitate arm rotation, lifting, and stabilization. Strong deltoids contribute to shoulder health and prevent injuries related to overhead movements.
3. Latissimus Dorsi and Trapezius: These muscles comprise the upper back, providing support and mobility for the shoulders and spine. The latissimus dorsi, often called the “lats,” enable pulling motions, while the trapezius assists in neck and shoulder movement.
4. Biceps and Triceps: Located in the arms, the biceps brachii are responsible for flexing the elbow, while the triceps brachii extend the elbow. Balanced training of these muscles ensures arm strength and functionality.
Core Muscles
The core muscles are essential for stability, posture, and functional movement. This group includes the abdominals, obliques, and lower back muscles, all of which contribute to maintaining spinal alignment and reducing injury risk.
1. Rectus Abdominis: Commonly known as the “six-pack” muscles, the rectus abdominis plays a significant role in trunk flexion and maintaining abdominal pressure.
2. Obliques: The internal and external obliques assist in rotational movements and lateral flexion of the trunk, contributing to overall core strength and stability.
3. Erector Spinae: This group of muscles along the spine aids in extending and stabilizing the back. Strengthening the erector spinae prevents lower back pain and supports proper posture.
Lower Body Muscles
The lower body consists of some of the most powerful muscles in the human body muscle diagram. These muscles are responsible for locomotion, balance, and force generation in activities such as running, jumping, and lifting.
1. Quadriceps: The four muscles of the quadriceps—rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius—are responsible for knee extension and hip flexion, playing a crucial role in walking and sprinting.
2. Hamstrings: The hamstring muscles, located at the back of the thigh, control knee flexion and hip extension. They are essential for explosive movements and injury prevention in athletes.
3. Gluteal Muscles: The glutes, including the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus, contribute to hip stability, posture, and lower body strength.
4. Calf Muscles: The gastrocnemius and soleus make up the calf muscles, which facilitate plantar flexion and aid in movements such as jumping and sprinting.
The Importance of Strength Training and Muscle Health
Maintaining muscle health is crucial for overall well-being, mobility, and longevity. Strength training, proper nutrition, and adequate recovery all contribute to optimal male musculature. Resistance training helps in hypertrophy, improving both muscular endurance and strength. Additionally, ensuring sufficient protein intake and hydration supports muscle repair and growth.
Incorporating exercises that target different muscle groups ensures balanced development and minimizes injury risk. Compound movements such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses engage multiple muscles simultaneously, leading to efficient and effective workouts. Understanding the male anatomy muscles and bones through a detailed study of the human body muscle diagram enhances the ability to design effective fitness routines tailored to individual goals.
Frequently Asked Questions: Understanding Male Musculature and the Human Body Muscle Diagram
1. Why is it important to understand the human body muscle diagram for strength training?
Understanding the human body muscle diagram allows individuals to target specific muscle groups effectively, ensuring balanced strength development and reducing injury risks. When designing a workout regimen, recognizing how muscles interact can enhance performance by optimizing movement efficiency and promoting proper biomechanics. This knowledge also aids in identifying muscle imbalances, which can lead to postural issues or increased strain on joints. Additionally, a well-informed approach to training improves recovery times, as individuals can implement strategies that target supporting muscle groups and minimize overuse injuries. Strength training without a foundational understanding of male musculature may lead to inefficient workouts, limiting progress and increasing the likelihood of injuries over time.
2. How do muscles and bones work together to support movement in the male body?
Male anatomy muscles and bones function in a coordinated system where muscles contract to produce movement by pulling on bones. This intricate relationship is facilitated by tendons, which connect muscles to bones and allow for smooth, controlled motion. Joints serve as pivot points where movement occurs, and ligaments provide stability by limiting excessive motion that could result in injury. The body’s ability to generate power, maintain balance, and execute complex movements depends on the strength and coordination of these interconnected systems. Understanding the human body muscle diagram helps illustrate the alignment of muscles and bones, providing valuable insight into how to improve mobility, flexibility, and overall physical performance.
3. What role does male musculature play in metabolic health?
Muscle tissue is metabolically active, meaning that a higher percentage of muscle mass contributes to an increased resting metabolic rate (RMR). This means that individuals with well-developed male musculature burn more calories even when at rest, which supports weight management and overall metabolic health. Additionally, muscles serve as primary sites for glucose uptake, helping regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes. Strength training that engages various muscle groups, as depicted in a body muscle diagram, enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes efficient energy utilization. The more muscle mass an individual maintains, the better their body functions in managing energy expenditure, reducing fat accumulation, and supporting long-term metabolic health.
4. How can an understanding of the male anatomy muscles and bones prevent injuries?
Injury prevention relies on a balanced and well-functioning musculoskeletal system, where muscles and bones work together harmoniously. Weak or underdeveloped muscles increase the likelihood of joint instability, leading to strains, sprains, or even fractures. By studying a human body muscle diagram, individuals can identify which muscle groups require strengthening to provide better support for their skeletal structure. Strengthening stabilizing muscles, particularly those surrounding joints such as the knees, shoulders, and lower back, significantly reduces the risk of injury. Additionally, proper stretching and mobility exercises, informed by an understanding of male musculature, enhance flexibility and allow muscles to perform at their optimal capacity, minimizing the likelihood of tears or overuse injuries.
5. Are there differences in male and female musculature, and how do they impact training?
While both males and females have the same muscle groups, differences in hormone levels, particularly testosterone, influence the development of male musculature. Males typically have a higher percentage of lean muscle mass and greater muscle fiber density, which contributes to increased strength and power output. This distinction affects training approaches, as men often respond more rapidly to resistance training in terms of muscle hypertrophy. However, both men and women benefit from strength training, and incorporating compound exercises targeting major muscle groups, as indicated in a body muscle diagram, is crucial for balanced development. While men may focus on maximizing muscle size and strength, women often emphasize muscle endurance and functional fitness, though both approaches contribute to overall health and injury prevention.
6. What are the best exercises to develop a well-balanced male musculature?
Developing a well-balanced male musculature requires a combination of compound and isolation exercises that target all major muscle groups. Compound movements such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups engage multiple muscles simultaneously, promoting overall strength and coordination. Isolation exercises like bicep curls, triceps extensions, and leg curls focus on specific muscles, ensuring balanced development and addressing weak points. Understanding the human body muscle diagram allows individuals to tailor their workouts by identifying underdeveloped areas that require additional attention. Additionally, incorporating functional movements that mimic real-life activities enhances muscle efficiency and prevents imbalances that could lead to injuries.
7. How does age affect muscle mass, and what can be done to maintain it?
As individuals age, they naturally experience a decline in muscle mass, a condition known as sarcopenia. This process begins as early as the 30s and accelerates with age, leading to decreased strength, mobility issues, and a higher risk of falls. Engaging in regular resistance training, as guided by a body muscle diagram, helps slow down muscle loss by stimulating muscle protein synthesis. Adequate protein intake, combined with proper recovery and a nutrient-rich diet, further supports muscle maintenance and repair. Additionally, engaging in activities that challenge coordination and balance, such as yoga and functional training, ensures that male musculature remains strong and resilient well into old age.
8. What are the long-term benefits of strengthening male anatomy muscles and bones?
Strengthening male anatomy muscles and bones provides long-term benefits beyond physical aesthetics, significantly enhancing quality of life. Strong muscles support joint health by reducing stress on ligaments and cartilage, minimizing the risk of arthritis and chronic pain conditions. Increased bone density, achieved through weight-bearing exercises, reduces the risk of osteoporosis and fractures later in life. Moreover, a well-conditioned musculoskeletal system contributes to better posture, reducing the likelihood of developing spinal misalignments or discomfort. Understanding the human body muscle diagram allows individuals to take a proactive approach to maintaining musculoskeletal health, ensuring longevity and an active lifestyle well into advanced age.
9. How do nutrition and hydration impact muscle growth and recovery?
Muscle growth and recovery rely on proper nutrition and hydration, as these factors influence muscle protein synthesis and repair. Consuming an adequate amount of protein provides the essential amino acids necessary for muscle tissue regeneration after exercise. Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source for training sessions, replenishing glycogen stores and preventing muscle fatigue. Hydration is equally critical, as dehydration impairs muscle function, reduces strength output, and increases the risk of cramps and injuries. By integrating insights from a human body muscle diagram, individuals can optimize their nutrition strategies to support the specific demands of different muscle groups, ensuring efficient recovery and sustained performance.
10. Can flexibility and mobility training enhance male musculature?
Flexibility and mobility training are essential components of a well-rounded fitness program, contributing to the optimal functioning of male musculature. Tight muscles can lead to restricted movement patterns, increasing the risk of compensatory injuries and imbalances. Dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching post-exercise help maintain muscle elasticity and prevent stiffness. Mobility exercises, such as joint rotations and controlled movements, improve the range of motion and enhance overall functional strength. Incorporating these strategies, alongside strength training informed by a human body muscle diagram, ensures that the male musculoskeletal system remains resilient, capable, and adaptable to various physical demands.
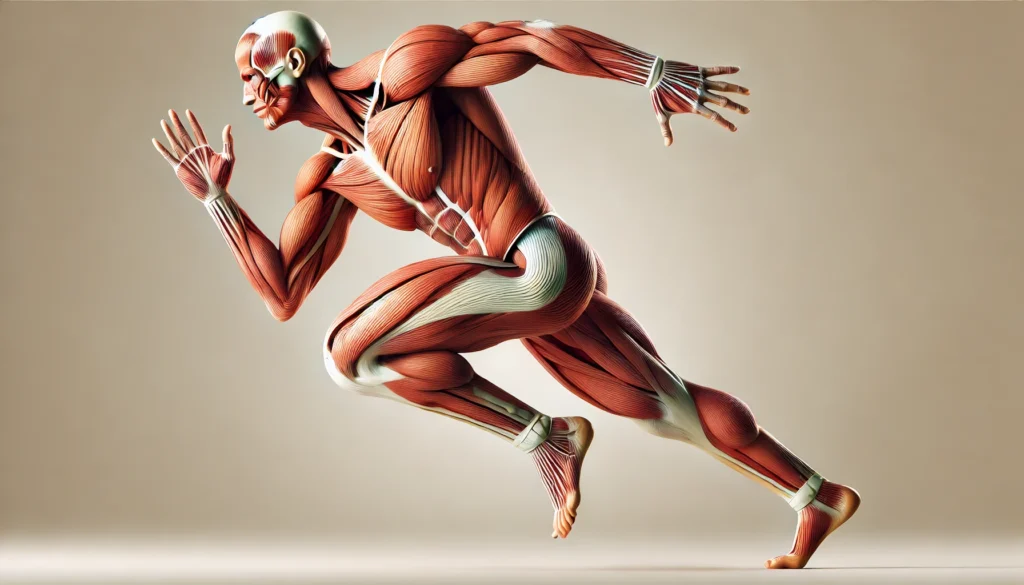

Conclusion
A deep understanding of male musculature provides invaluable insight into movement mechanics, strength training, and overall physical health. The human body muscle diagram serves as an essential reference for learning about major muscle groups and their functions. Whether your goal is to improve athletic performance, prevent injuries, or build muscle mass, knowledge of male anatomy muscles and bones empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their fitness and health. By prioritizing proper exercise, nutrition, and recovery strategies, one can optimize muscular health and maintain long-term physical vitality.
muscle anatomy guide, skeletal muscle structure, upper body strength training, lower body muscle groups, core stability exercises, functional muscle movement, strength training for men, bodybuilding fundamentals, athletic performance optimization, injury prevention techniques, muscle recovery strategies, muscle hypertrophy principles, biomechanics of movement, weightlifting techniques, flexibility and mobility training, posture correction exercises, resistance training benefits, metabolic health and muscle, exercise science insights, human physiology and fitness
Further Reading:
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While News7Health strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. News7Health, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of News7Health.

